In most cases, the human papillomavirus in men is not life-threatening. Once in the body, HPV provokes the appearance of benign formations. But there are seals that have a high oncogenic degree. The development of this strain is the first stage in the formation of oncology. The onset of a fatal disease can be accidentally "missed. "Its origin occurs in the upper layer of the epidermis and does not manifest itself for a long time.
Types of papillomavirus
There are a huge number of papillomaviruses. Some species have not yet been thoroughly studied. If you become infected with one type, you can acquire a harmless wart, while with another you can get a malignant formation and cancer. Papillomas in men on the head of the penis are the subject of special attention, since there is a high risk of developing cancer.
The classification of HPV strains is divided into three categories, according to the ICD:
- Non-oncogenic group (types 1-3, 5). They mostly pass due to the resistance of the human immune system. They never become malignant.
- Low risk viruses. Transmitted through traditional sexual contact. In the presence of favorable conditions for development, in quite rare cases, they can become the initial stage of the oncological process. This type includes: 6, 11, 42-44.
- High percentage of "severe" pathology. This class of pathogens often becomes a provocateur of malignant genitourinary formations. The most dangerous of them are types 16 and 18, which contribute to the development of genital cancer in men and cervical cancer in sexual partners.
It is important to know! Of particular note are strains of types 13, 31, 33 and 35. Their danger lies in the development of genital warts in intimate places. A sign of other, no less serious infections is a rash (58, 39. 52, 30, 42, 43, 59, 55, 57, 40, 61, 62 and 67-70).
Features of the development of papillomas in the male body
When entering the human body, the papilloma virus always goes through the same stages of development:
- Latent stage. The disease does not manifest itself in any way by external symptoms. Its presence can be diagnosed only by PCR.
- Clinical phase. Various formations appear as a result of increased cell division.
- Dysplasia is a progressive stage. Deformation of the cellular structure occurs.
- Carcinoma - the papillomavirus integrates, a malignant mutation of the DNA code occurs. Invasive cancer develops.
Genital warts that occur in the bikini area, testicular sac, head of the penis and foreskin require immediate treatment. Such growths negatively affect a man’s personal life, provoke health problems for his wife, and contribute to the development of papillomatosis in the unborn child. They can also become malignant. Sometimes condylomas are a symptom of sexually transmitted diseases that have not fully revealed themselves (for example, syphilis).
Routes of infection
The most common way to acquire HPV is through sexual contact with a carrier of the virus. In this case, the form of intimate communication does not matter. The household route of infection is much less common. There is a risk of infection when visiting public places:
- Swimming pools, baths, saunas - pathogenic microbes are easily transmitted from the host, penetrating through abrasions and scratches.
- Hairdressing and beauty salons - the risk of infection is in inverse proportion to the handling of instruments.
- Surgical and dental interventions can contribute to infection.
Maximum protection is maintaining basic personal hygiene: both in your own home and outside the home. Barrier methods of contraception can significantly reduce the risk of the disease.
Favorable conditions for progression
After entering the male body, the virus remains in "sleeping" mode for a long time. The following reasons can "activate" it:
- Weakened immunity after a long illness.
- The presence of regular physical or emotional "overload. "
- Exhaustion of the body due to severe stress.
- Various venereal pathologies.
- Increased sweating.
A dangerous feature of HPV is that the characteristic symptoms do not appear at the initial stage of the disease, but at its "height". What prevents the identification of threatening strains in the early stages.
Complex of symptoms

Emerging formations with HPV have their own distinctive nuances. To exclude the presence of other, similar diseases, it is necessary to carefully analyze the clinical "picture". So, signs of the papilloma virus in men:
- Acrochords or threadlike papillomas on the stalk. Usually flesh or dark brown in color. Reach a size of 5 mm. They appear on the neck, face, scrotum and testicles, groin and armpits. They often get injured.
- Flat growths are a collection of nodules that have a shiny surface without folds. Has a beige or pinkish tint. Usually the size does not exceed 8 millimeters. The affected areas are the shins, hands, and forearms.
- Condylomas on the head in men are grayish pointed plaques on a stalk. There are single and multiple. Frequent areas of "habitat" for growths are the pelvis and genitals. Often the anus becomes blocked, causing burning, itching, and bleeding.
- A spine is a round formation that appears on the outside of the palms and soles. If left untreated, after a few weeks they become rough and a black dot appears in the center.
- Common (simple, vulgar) warts. They appear simultaneously as a whole group. The maximum size is 10 mm. Usually the knees, hands, and fingers "suffer. "
The earlier treatment for papillomavirus is started, the greater the chance of avoiding serious health consequences.
Dangerous consequences
Statistical data report rare cases of cancer development due to HPV in men. An alarming factor are formations on the surface of the penis and pubis. At any moment they can develop into a malignant form. Other pimples, for example on the back, in the mouth, should also be responded to with adequate measures.
Attention! If papillomavirus manifestations are left untreated for a long time, they can develop into melanoma - skin cancer.
Establishing diagnosis
How to treat papillomas on the head of the penis? Visiting a dermatologist is the first step towards healing. The initial appointment with a specialist includes a thorough visual examination of the mucous membranes and skin. A detailed survey of the patient is also conducted, and individual complaints are listened to.
If the presence of a virus is suspected, the patient is sent for additional examination:
- Blood and discharge from the bladder are donated for analysis. Based on the obtained indicators, the causative agent of the virus is isolated from the general DNA material.
- A biopsy of condylomas is performed. The result determines the presence or absence of cancer cells.
- A cytological examination of the mucous membranes is performed.
- Sometimes ureteroscopy is required.
After the final history, the doctor makes a conclusion and determines the treatment complex.
Treatment for men
It is impossible to completely get rid of HPV, like the herpes virus. Treatment of papillomas in men is as follows: all therapeutic and surgical measures are aimed at leveling the manifestations of the pathology and increasing the period of remission.
Specialist who will help
To develop optimal tactics to combat papillomavirus, it is necessary to undergo examination by a number of specialists. (Venereologist, proctologist, urologist and, if necessary, oncologist). At first, you can contact your local therapist, who will coordinate your further actions.
Removal of papillomas
When identifying viruses of types 16 and 18, removal of all kinds of growths is a must. After which a course of drug therapy is prescribed, which is able to suppress the causative agent of the disease and at the same time maximize the body’s natural defenses. A radical method of getting rid of papillomas is used if conservative treatment does not lead to the desired result.
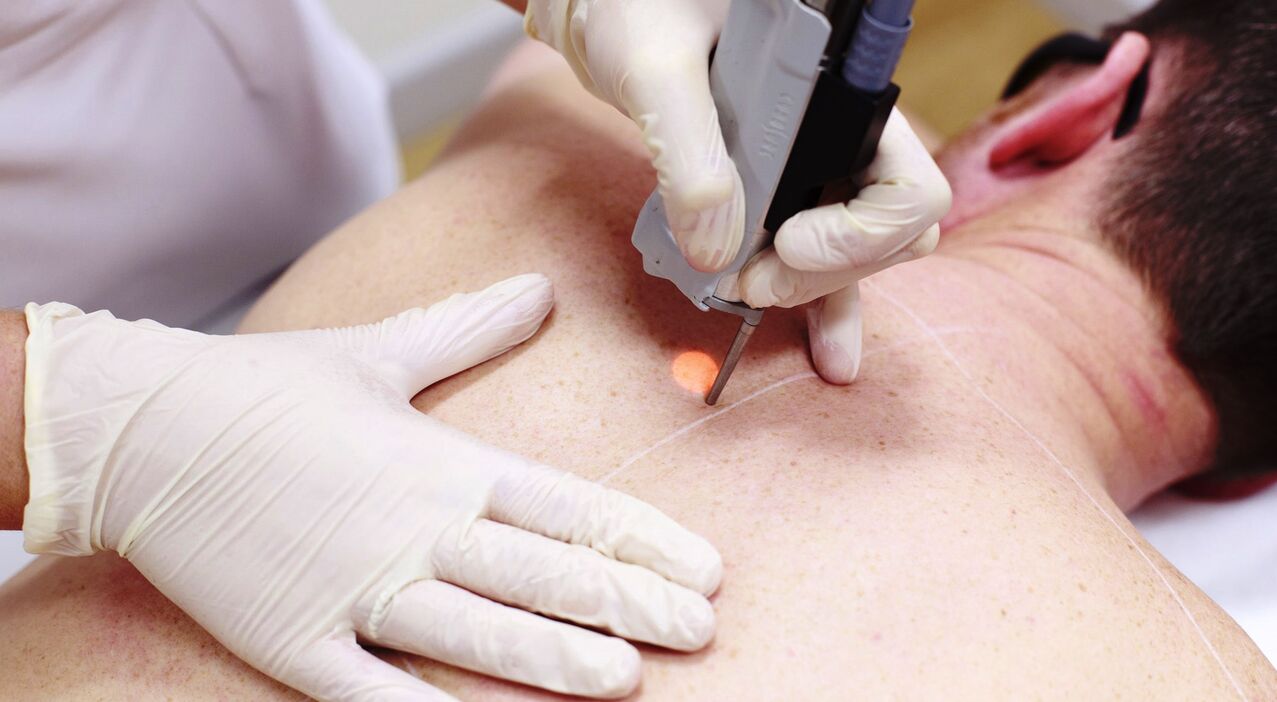
The procedure is carried out in different ways:
| Type of intervention | Method of implementation | Purpose and features of the procedure |
|---|---|---|
| Surgery | The tool is an ordinary scalpel. The choice of anesthesia depends on the affected area, medical prescription and the wishes of the patient. | Used mainly for oncological papillomas. |
| Laser | With the help of infrared rays, pathological growths are "burned out". | It is characterized by minimal complications and the possibility of complete removal of damaged tissue. |
| Excision using a radio knife | Impact on education with high-frequency waves. | An effective, fast and painless way. Often used to remove papillomas under the head of the penis. |
| Electrocoagulation | Impact of electric current on papilloma. | It is distinguished by a protracted healing process (up to two weeks). A painful method, according to customer reviews. Subsequently, a scar remains. |
| Cryodestruction | Liquid nitrogen is used. | Based on patient comments, this is a rather inconvenient method. |
| Chemical methods | Local use of various synthetic agents. | Do not use on overly sensitive areas of the body, such as the head of the penis. Damage to healthy tissues is also possible. |
Attention! It is strictly forbidden to get rid of papilloma yourself at home or to smear it with iodine. Such damage can lead to a transition from a benign tumor to a cancerous tumor.
Other therapeutic methods
Conservative treatment of papillomavirus in representatives of the stronger sex consists of taking medications.
Typically, specialists prescribe the following drugs:
- Stopping increased cell division: creams, ointments.
- Local agents on a natural basis (celandine) are sold in pharmacies at an affordable price.
- Promoting the activation of independent synthesis of interferons in the patient’s body.
- Immunomodulatory tablets.
- Antiviral drugs.
The dosage, regimen, and duration of the course are determined only by the attending doctor. During therapy, qualified monitoring of the effectiveness of the chosen tactics and timely detection of possible allergic reactions is necessary. Any virus cannot be treated with antibiotics. The need for their use is taken into account by the doctor, depending on the course of the disease. The use of folk recipes for HPV in no case can replace medical prescriptions. The use of various herbal decoctions is possible subject to prior consultation with a specialist. This fact should not be ignored if there are chronic intestinal pathologies.
Prevention of papillomas
Preventive measures for the papilloma virus are possible without special knowledge and skills. Conditions for a healthy lifestyle, monogamous relationships, and personal hygiene are available to every person. Modern scientists have developed several vaccines, vaccination with which significantly reduces the risk of developing HPV with a high oncogenic potential (6, 11, 16 and 18). The vaccine, consisting of two elements, is designed to prevent the most dangerous strains. The most suitable age for vaccination is considered to be between 10 and 25 years. The effective period of the vaccine is approximately 6. 5 years. Vaccinations are suitable for both girls and boys.
Conclusion
So that at one "wonderful" moment you do not have to face the problem of how to get rid of papillomas, you need to remember about precautions. Protected sexual intercourse, alas, is not always a guarantee of good health. Regular preventative medical examination will help. Whether vaccinations are needed is up to everyone to decide for themselves. But if there are proven means that protect against the possibility of a fatal disease, then it would be a sin not to use them.















